In today’s fast-paced digital world, QR codes have become ubiquitous, revolutionizing the way we interact with information and businesses. From marketing campaigns to contactless payments, these pixelated patterns have found their way into various aspects of our lives, offering convenience and efficiency like never before.
Introduction to QR Codes
What are QR codes?
QR codes, short for Quick Response codes, are two-dimensional barcodes that store information in a square grid of black squares on a white background. Originally developed in Japan in the 1990s by Denso Wave, a subsidiary of Toyota, QR codes were created to track automotive parts during manufacturing. Since then, they have evolved into a versatile tool for encoding various types of data.
Historical background
The history of QR codes dates back to 1994 when Denso Wave patented the technology. Initially used for tracking parts in the automotive industry, QR codes gained popularity due to their ability to store large amounts of data compared to traditional barcodes. Over the years, advancements in technology have made QR codes more accessible and widely used across different industries.
How QR Codes Work
Structure of QR codes
QR codes consist of black modules arranged in a square grid on a white background. These modules represent binary data, which can encode alphanumeric characters, binary data, or even kanji characters. Additionally, QR codes contain positioning markers and timing patterns that allow scanning devices to interpret the data accurately.
Encoding data
QR codes can store various types of data, including URLs, text, contact information, and more. The data is encoded within the QR code using a specific encoding algorithm, such as the Reed–Solomon error correction code, which ensures data integrity even if the code is partially damaged or obscured.
Applications of QR Codes
Marketing and advertising
QR codes are widely used in marketing and advertising campaigns to provide consumers with quick access to additional information or promotional offers. By scanning a QR code printed on a poster, flyer, or product packaging, users can instantly access websites, videos, or special discounts, enhancing their engagement with the brand.
Contactless payments
In the era of digital wallets and mobile payments, QR codes have emerged as a popular method for facilitating contactless transactions. Merchants can generate QR codes that represent payment details, allowing customers to scan the code with their smartphones and complete the transaction seamlessly.
Ticketing and boarding passes
QR codes have simplified the process of ticketing and boarding passes for events, transportation, and flights. Instead of printing physical tickets, organizers and airlines can issue QR code-based tickets that users can conveniently store on their smartphones and present for scanning at the point of entry.
Inventory management
In industries such as retail and logistics, QR codes are used for inventory management and tracking. Each product or package can be assigned a unique QR code, which contains information about its origin, destination, and status. Scanning QR codes enables real-time visibility and control over inventory levels and movements.
Benefits of QR Codes
Convenience
One of the key benefits of QR codes is their convenience. With a simple scan using a smartphone camera or QR code reader app, users can access relevant information or complete transactions without the need for manual data entry or typing URLs.
Versatility
QR codes are incredibly versatile and can be used in various applications across different industries. Whether it’s for marketing, payments, ticketing, or inventory management, QR codes offer a flexible solution for encoding and accessing data efficiently.
Cost-effectiveness
Compared to traditional methods such as printed materials or physical tokens, QR codes are a cost-effective solution for businesses. Generating and distributing QR codes is relatively inexpensive, making them an attractive option for organizations looking to streamline operations and enhance customer experiences.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Risks associated with QR codes
While QR codes offer numerous benefits, they also pose certain security and privacy risks. Malicious actors can exploit QR codes to redirect users to phishing websites, download malware onto their devices, or steal sensitive information. It’s essential for users to exercise caution when scanning QR codes from unknown sources.
Best practices for safe scanning
To mitigate the risks associated with QR codes, users should follow best practices for safe scanning. These include verifying the source of the QR code, using reputable QR code scanning apps, and avoiding scanning codes that appear suspicious or unfamiliar.
QR Code Generation and Scanning
Tools and software for creating QR codes
There are various tools and software available for creating QR codes, ranging from simple online generators to advanced QR code management platforms. These tools allow users to customize the appearance and functionality of QR codes and track their performance through analytics.
How to scan a QR code
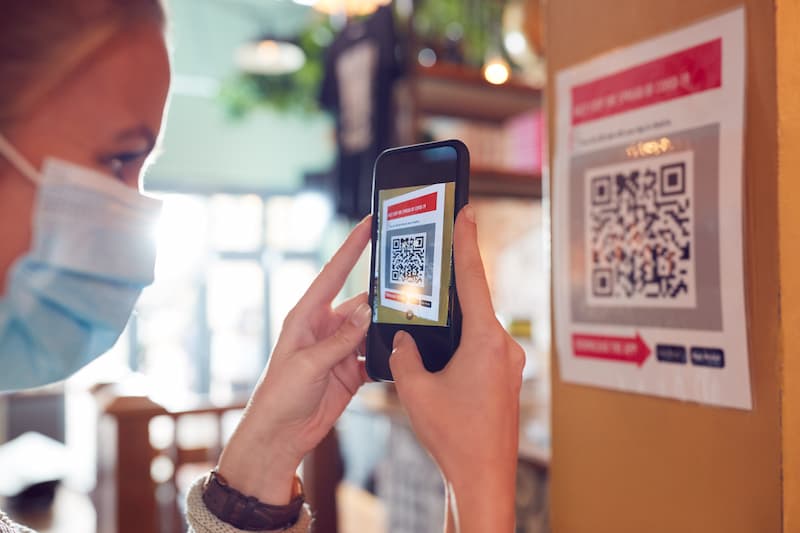
Scanning a QR code is a straightforward process that can be done using a smartphone camera or a dedicated QR code scanning app. Users simply point their device’s camera at the QR code, and the corresponding content or action is automatically triggered, whether it’s opening a website, making a payment, or adding contact information.
QR Codes in the Digital Age
Integration with smartphones and apps
With the widespread adoption of smartphones and mobile apps, QR codes have seamlessly integrated into the digital ecosystem. Most smartphones come equipped with built-in QR code scanning functionality, allowing users to scan codes directly from their camera app or through third-party QR code reader apps.
Future trends and innovations
As technology continues to evolve, QR codes are expected to evolve as well, with new features and innovations on the horizon. From enhanced security measures to augmented reality integration, the future of QR codes holds exciting possibilities for further enhancing digital interactions and experiences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, QR codes have emerged as a powerful tool for facilitating digital interactions and enhancing user experiences across various industries. From marketing and payments to ticketing and inventory management, QR codes offer unparalleled convenience, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. However, it’s essential for users to remain vigilant against security risks and follow best practices for safe scanning to ensure a seamless and secure experience.












Got a Questions?
Find us on Socials or Contact us and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.